The number of cases of coronavirus infection in Armenia has been increasing since July. On the 12th and 18th of the same month, they amounted to 3.4 million worldwide, an increase of 12% compared to the previous week, and new variants of the virus continue to appear in different countries, one more dangerous, the other less dangerous.
In recent months, a new variant of the virus, Delta Plus, has emerged, and scientists are trying to figure out whether it is more dangerous than its already well-known friend Delta, which has been the cause for thousands of deaths in India and is becoming the increasingly prevalent variant around the world.
Acting Minister of Health Anahit Avanesyan told reporters on July 26 that there is currently no sequenced specimen of the Delta strain in Armenia, but that it is circulating because we have an open border with both Russia and Georgia, where that strain is found. The Acting Minister also mentioned the possibility of a launch of the fourth wave of Covid-19 in the country.
This material summarizing the evolution of SARS-Covid-19 will help to avoid confusion and differentiation of modifications from one another, completing the chronological sequence of their occurrence.
What is a strain?
Strain = variant = modification

All viruses change over time, mutating, including SARS-CoV-2, which is responsible for the spread of the Covid-19 disease. Most of the changes have little or no effect on the properties of the virus and may even weaken it, but they are not ruled out and can lead to:
- An increase in the likelihood of viral infection
- The severity of the associated disease
- A decreased efficacy of vaccines and drugs
- The violations of diagnostic tools or other social and public health norms.
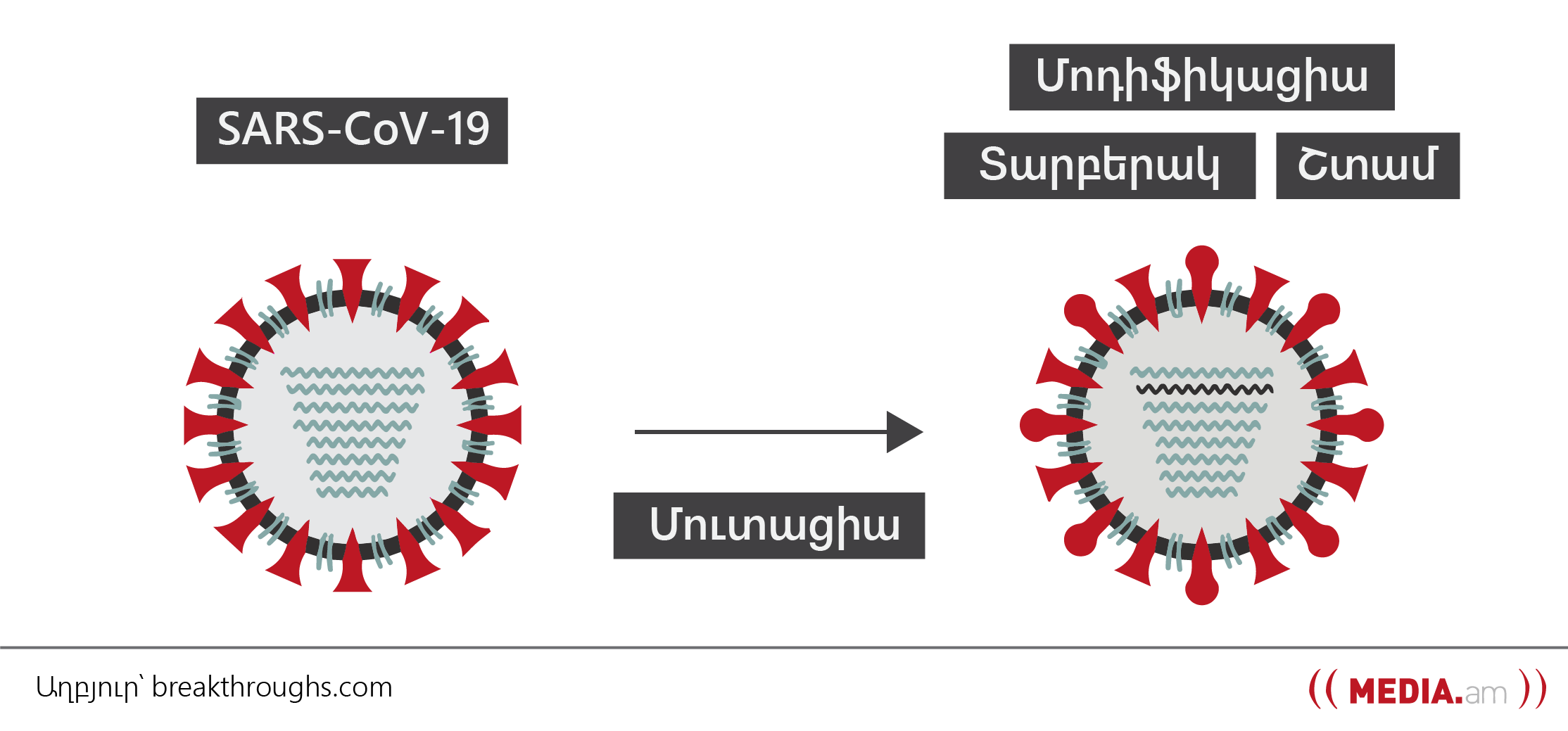
Why do viruses mutate?
The process of mutation occurs during the multiplication of the virus, when, using the mechanisms of its new host cells, the virus is duplicated and copied. The mistakes made during that copy are the mutations from which new variants of the virus are formed.
According to David Wall, professor of infectious diseases at the University of North Carolina Medical School, viruses are introduced in order to “live longer.” The human immune system creates a lot of barriers for viruses to prevent them from penetrating our body. According to Wall, viruses are modified to resist the human immune system rather than to “beat” drugs and vaccines.
Classifications
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been monitoring and evaluating the evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus since January 2020 with its partner institutions, researchers and professionals. The emergence of new and more dangerous variants of the virus in late 2020 prompted them to be classified into the following groups:
- Variants of Interest (VOIs)
Genetically modified variants of SARS-CoV-2 that have or are predicted to have changes in traits such as infectivity, disease severity, immune bypass, diagnosis and treatment.
- Variants of Concern (VOCs)
They are endowed with interesting features, are relatively more dangerous and contagious, are more difficult to diagnose, treat, and prevent with vaccines.
* There are also options for Strong Consequences, but to date, SARS-CoV-2 has not achieved this.
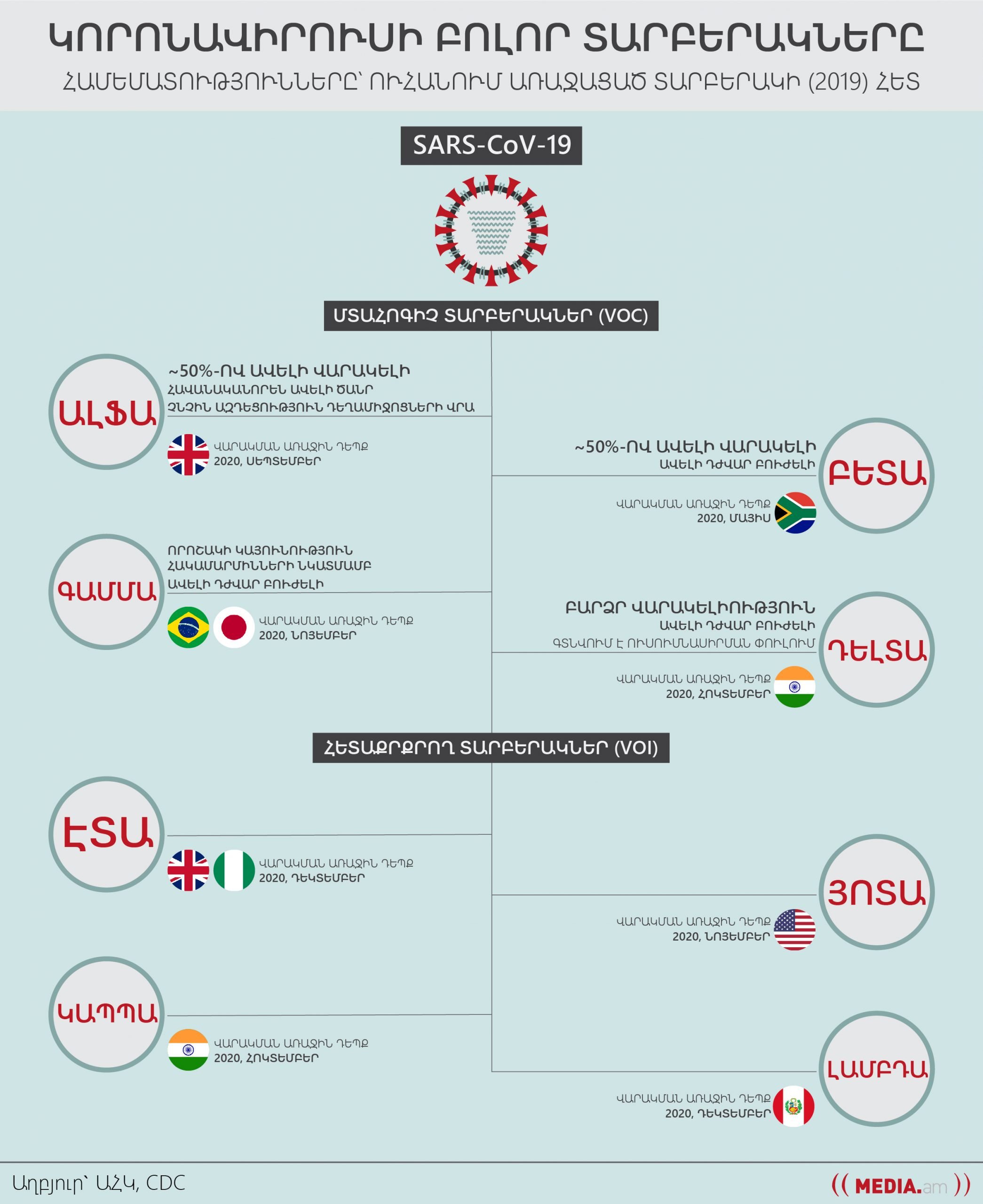
And where is Delta Plus?
Delta Plus is a modified variant of the Delta strain with the K417N mutation. It appeared in the world databases in the middle of March of this year, and already on April 26 the first cases of infection with it were registered in England. Although this strain is not very common, the Indian Ministry of Health has classified it as a Concern Option (VOC), citing its high infectivity, stickiness and potential for antibody resistance. However, it is not yet clear whether Delta Plus reaches the level of the Concerned variant.
“India has called it a matter of concern, not out of precision,” said Ravindra Gupta, an infectious disease specialist at the University of Cambridge.
A total of 200 cases of the Delta Plus strain infection have been reported in 11 countries, one of which (India) ended in death.
Why Alpha, Beta ․․․?
Experts invited by the WHO advised naming the strains according to the letters of the Greek alphabet: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, etc. According to them, it is easier to remember and present what variant of the virus it is to the public.
How is each new strain different from the other?
Scientists are paying close attention to changes in the Peplomers of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Peplomers are the prickly outer layer of virus RNA that attach to the receptors on human cells.
R0 – Infection
Virus infectivity is measured by R0, which is the virus replication index. It shows how many people a virus carrier can infect. When we say that the R0 of the Covid-19 Alpha variant is equal to 2-4, it means that a person infected with this strain can infect 2-4 people who do not follow the anti-epidemic rules. The higher the R0, the more contagious the virus is.

Do current vaccines protect against new variants?
Existing vaccines are effective against Delta, but only after taking the full dose. According to a study by Public Health England, the first dose of Pfizer and AstraZeneca vaccines protects against the disease caused by the Delta variant by 33%. After two doses, AstraZeneca alone is 60% effective and Pfizer is 88% effective.
For safety reasons, the WHO still advises fully vaccinated people to wear masks, otherwise they may become part of the spread of the virus.
Will the new strains form endlessly and will it be harder and harder to fight them each time?
“The fact that in 18 months the virus has mutated into two strains (Alpha and Delta) that are 50% more contagious than each other is an incredible change,” said Aris Katzurakis, of Oxford University.
He thinks that it is impossible to set numbers and predict how much it will increase, but he assumes that the infectivity will continue to increase in the next few years.
“It does not mean that we will consume the Greek alphabet and reach omega, which will become an invincible monster. It is still very difficult to predict what is the best strategy against the coronavirus,” said Katzourakis.
Options in Armenia and the region
Information from the WHO regarding a fourth wave of the epidemic and the spread of the Delta variant in the region became an occasion for the RA Ministry of Health to impose restrictions. According to the Ministry of Health, in neighboring Georgia and Russia (accounting for 88.5% of studies), this strain is widespread, which is characterized by an unprecedented rapid spread and a more severe course of the disease.
The Ministry of Health then issued two awareness messages, the first being a Reuters report on how a number of countries, due to the spread of the Delta variant, were forced to adopt making vaccinations mandatory for health care workers and people at risk. The second was the material summarizing the Delta strain of the National Center for Disease Control and Prevention of the RA Ministry of Health and summarizing the rules for avoiding infection.
So what?
It is difficult to make an assessment and make predictions about how Covid-19 will develop and how much and how many strains will be formed. Perhaps the most reassuring in this anti-epidemic and information boom is the scientists’ assessment that for the viruses to spread more easily they need to weaken.
Christian Ginosyan